Your challenge. Leverage AWS to become a smart factory and improve business operations.
Smart factory is within reach.
Companies need a plan and a tech solution to use autonomous and collaborative robotics in production, do real-time inventory and production tracking, perform predictive maintenance or support the health and well-being of their workers on the shop floor.
How we do it Harness your edge devices data and enable them to act intelligently.
Build your 4.0 factory.
Connect every machine with edge computing technologies and benefit from a remote and global overview of your factory processes.
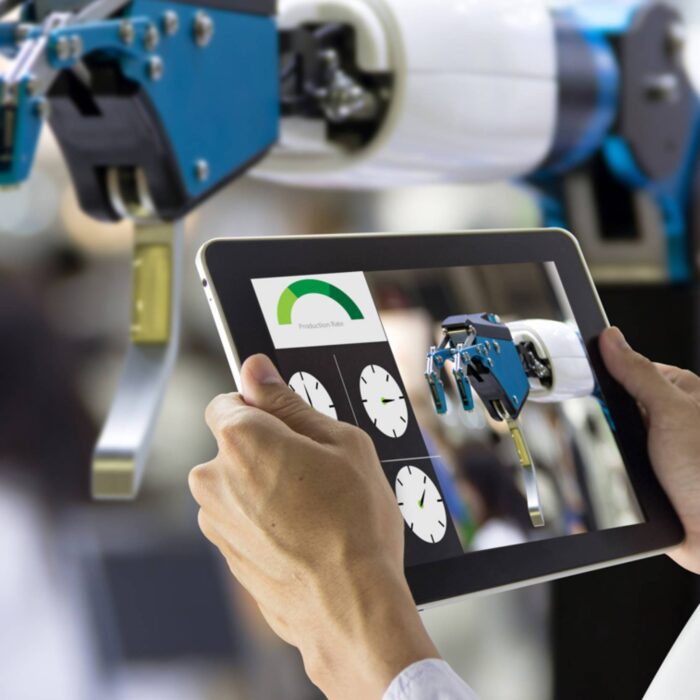
Analyze your machine data to visualize your factory pain points
Factory equipment has heterogeneous languages and protocols. Collect and translate machine data from the factory floor to the cloud and turn it into actionable insights to enhance overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Align business goals with IoT data and create efficient predictive models.
Analyse the company and production challenges to define the key criteria of business-oriented predictive models that will enhance global productivity.
Build predictive models to enhance productivity.
Benefit from a real-time digital representation of your factory production to reduce costs, waste and downtime. Make fast decisions to optimize your production and supply chain.
Talk to us. Ready to change how you work?
Edge computing means using devices that are physically located near the data source to do the data processing and storing. Rather than sending workloads to centralized data centers which are possibly thousands of miles away or relying on the cloud, edge computing makes use of local devices to do the heavy lifting. Only the results of the processes are sent on to the main data center or cloud, if needed.
It essentially depends on a local intranet of connected devices to process and store data instead of using the wider, external internet.
You can think of it like this: most large companies have a main headquarters, but they also operate several branch offices nearer to their customers to better serve them.
Edge computing takes advantage of the fact that these local devices “on the edge of the cloud” have more space and resources available and leverages the proximity to a client’s data source to reduce waiting times and bandwidth demands, providing near instant data analysis.
Edge computing is a type of decentralized information technology (IT) architecture that processes a client’s data on the edge of the cloud network, whether on site or at a nearby satellite data center.
By relying on smaller, closer computers to do the bulk of the work, edge computing saves bandwidth and improves response times. Its inherent low latency allows for near real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization of operations.
Edge computing also minimizes the amount of data that needs to be processed by outside data centers. And since more data remains within your company’s own systems, edge computing also enhances your data security.
These benefits translate to lower costs and increased efficiency for your business.
Edge computing works by connecting your devices to a nearby edge device. Called an edge server, edge node or edge gateway, this device basically brings the cloud to you.
Different devices can serve as edge modules, from an employee’s on-premises laptop, desktop computer or smartphone to Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and connected manufacturing equipment.
Once the selected device is connected to the cloud, you have your own sort of satellite data center or cloud dedicated to crunching your data.
Thanks to its speed, edge computing is used to process time-sensitive data. This could range from monitoring machine health on the factory floor to studying and optimizing manufacturing logistics.
Since it brings the cloud to the client, edge computing is also useful in remote locations that have limited, or no, internet connectivity. It allows data to be processed on site instead of relying on poor or slow connections to transmit and analyze data.
The most basic example of edge computing is an in-home or in-office Wi-Fi network, where a router acts as an edge server and you can then connect multiple devices to the local network.
Beyond this simple use case, edge computing also has applications in factories, in retail stores and on agricultural sites.
Manufacturing businesses can connect their machines to an edge device to not only monitor production but also to automate processes, instructing equipment to take quick action based on the data they receive.
Retailers can use edge computing to improve the shopping experience through in-store customer tracking, real-time inventory management and near instantaneous point-of-sale data analysis.
In agricultural and farming applications, edge computing can be used to quickly and efficiently obtain data from environmental sensors or to coordinate the movement of heavy machinery.
Whatever your industrial use case may be, Devoteam can help your business harness the power of edge computing to reduce costs and increase efficiency.